Notes – Quadratics
Roots of the equation
Multiplying the equation both sides by , we get
Adding
to both sides
Sum and Product of the roots:
If and are the two roots of the above equation, then
Adding the above two,
Sum of the roots =
Product of the roots:
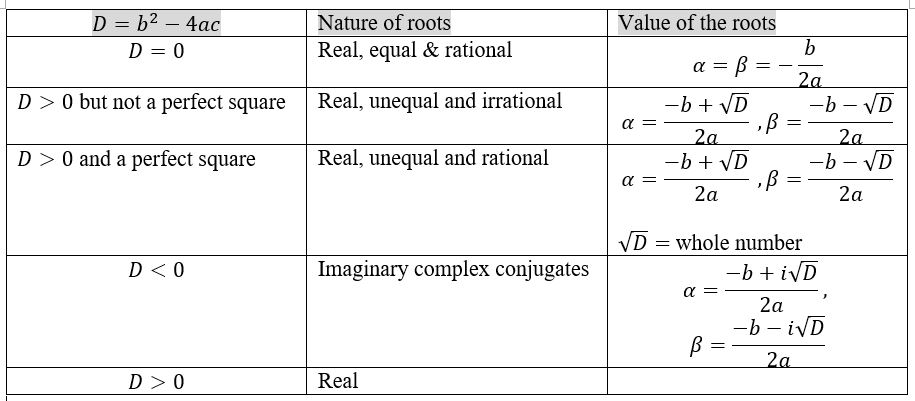
Nature of the roots:
Transformation of equations:
Let and are the roots of the equation
To find the equation whose roots are :
(i) Negative of the roots of the equation
The required roots are and .
This can be obtained by substituting
so,
or
(ii) Increased by i.e.
substituting
so,
so the required equation is
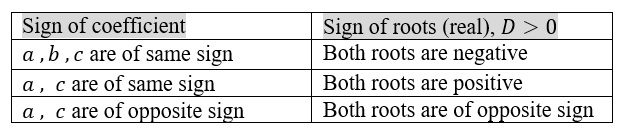
Sign of coefficient determining the sign of both real roots of